Facts
Research shows that victims of cardiac arrest have the best chance of survival when there is early access to CPR and defibrillation.
- In Canada, up to 45,000 people die of sudden cardiac arrest each year.
- The survival rate of victims from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is approximately 5%.
- Knowing how to respond to a cardiac arrest can increase the odds of survival and recovery by 30% or more.
- Almost 80% of all cardiac arrests occur in homes and public places and 35-55% are witnessed by a family member, co-worker, or friend.
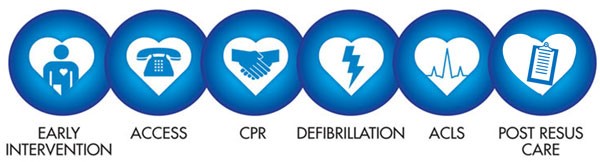
The Links in the Chain of Survival
The Chain of Survival depicts the critical actions required to treat life-threatening emergencies including heart attack, cardiac arrest, stroke, and foreign body airway obstruction. The links within this Chain of Survival include:
- Early Access to the emergency response system.
- Early CPR to support circulation to the heart and brain until normal heart activity is restored;
- Early Defibrillation to treat cardiac arrest caused by Ventricular Fibrillation; and
- Early Advanced Care by EMS and hospital personnel.
The first link, Early Access to the emergency response system, includes early recognition of the cardiac emergency and early notification of rescue personnel via a universal 1-1-2 telephone system (or 999 for the UK) as well as an internal alert system within specific facilities to trigger a response by designated trained and equipped personnel.
The second link, Early CPR, is a set of actions that the rescuer performs in sequence to assess and support airway, breathing and circulation.
The third link, Early Defibrillation, is the delivery of a shock to the heart to convert the heart’s rhythm from Ventricular Fibrillation back to a normal heart rhythm.
The fourth link, Early Advanced Care, relates to the response of highly trained and equipped pre-hospital EMS personnel (paramedics) who can respond to the patient and provide for the administration of drugs, advanced airway procedures, and other interventions and protocols, prior to the arrival of the patient at an advanced care facility.